"Wide color gamut" has become a trend among LCD displays recently. However, this "wide color gamut" is also a keyword that can easily lead to misunderstandings. We hope that a correct understanding of the color gamut of LCD displays will help you select products, use them daily, and make adjustments.
What is a color gamut?
A color gamut is a specific range of colors that are further defined within the range of colors that can be recognized by the human eye (visible range).
There are an infinite number of colors in nature, but digital cameras, scanners, displays, printers, and other color imaging devices all have different ranges of colors that they can reproduce, so color gamuts are determined to clarify these and to match colors between devices used.
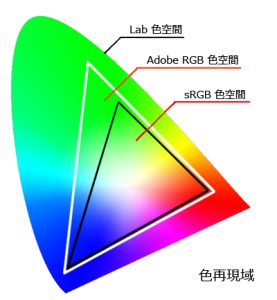
Just as the position of an object is expressed by combining multiple numbers called coordinates, color is expressed by combining multiple numbers, sometimes called color space. There are several ways to express (illustrate) a color gamut in an easy-to-understand way. In PC-related applications, three standards often appear: sRGB, Adobe RGB, and NTSC. The color gamut defined by each standard is shown as a triangle on the xy chromaticity diagram. When applied to LCD displays, the larger the triangle of the color gamut a product supports, the wider the range of colors that can be reproduced on the screen. Color gamut visible to the human eye: Lab color space (whole visible light spectrum)
Color gamut that can be expressed digitally: AdobeRGB, NTSC RGB color space (three primary colors of light, additive color mixture) Color gamut visible to the human eye: Lab color space (whole visible light spectrum) Color gamut that can be expressed digitally: AdobeRGB, NTSC RGB color space (three primary colors of light, additive color mixture)
What is the difference between Adobe RGB and NTSC RGB?
・Adobe RGB
This is the definition of RGB space proposed by Adobe Systems in 1998. Compared to NTSC RGB, some of the color gamut from green to red is wider. (See the image above) Most digital SLR cameras can shoot in a wide color gamut equivalent to Adobe RGB, and Adobe Photoshop, a representative retouching software from Adobe Systems, can correctly handle image data saved in the Adobe RGB color gamut.
High-quality inkjet printers can also print in the Adobe RGB color gamut.
When creating the above environment, the monitor on which the image is displayed must also have a wide color gamut equivalent to Adobe RGB to make the most of it.
Using an Adobe RGB-compatible monitor has the advantage that image data shot in Adobe RGB mode can be displayed in the correct color gamut on the monitor, and the accuracy of corrections can be improved.
Adobe RGB covers the color gamut of JMPA Color (Magazine Advertising Standard Color), which is one of the standard colors in the printing field, and Japan Color, so in the prepress market, if there is a monitor that can express Adobe RGB colors, the accuracy of soft proofing, which involves correcting colors on the monitor, can be further improved. For example, if the Adobe RGB coverage is 98%, 98% of the colors within the Adobe RGB color gamut can be displayed on the display.
・NTSC RGB
NTSC RGB is the international standard RGB space definition established by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). It is the standard color space for Windows environments, and websites are also created in accordance with sRGB.
NTSC RGB has the advantage of being highly versatile, as it is a color gamut that can be reproduced without any discomfort with general printers and cameras.
In addition, if you use a wide color gamut such as Adobe RGB when publishing photos or illustrations on the web, such as on social media, colors that cannot be reproduced depending on the display environment may be replaced, the color gamut may be compressed, and the colors may not be viewed as intended.
In addition, when printing photos you have taken online or at a photo printing store, wide color gamut data may not be printed correctly (except for some high-quality printing services), so using the sRGB color gamut will reduce the difference in the image with the finished product. The advantage of the sRGB color gamut is that it can convey the same image to everyone.
What did you think?
Today we explained the color gamut of displays.
Please use this as a reference for your future considerations.